By SPEAKIN’ OUT NEWS
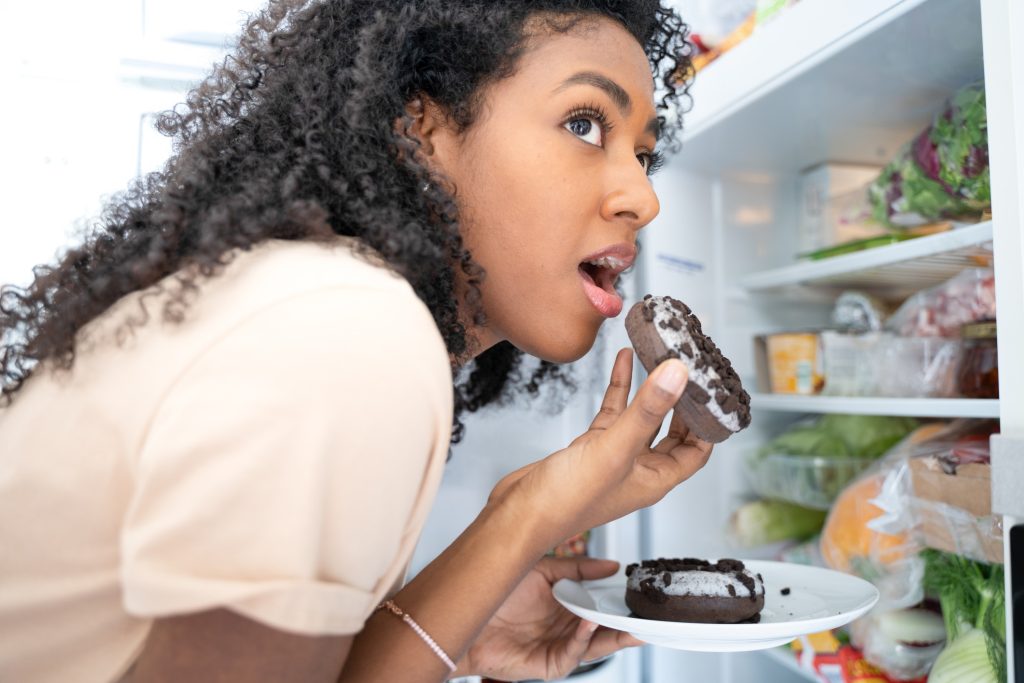

Food addiction is real — and science shows that certain foods can hijack your brain’s reward system in the same way addictive substances do. Here are six of the most irresistible offenders, according to research.
6. Chocolate: The “Gateway” Dessert
Chocolate is one of the world’s most studied and craved sweets. It contains compounds like theobromine, phenylethylamine, and caffeine, which stimulate the brain’s pleasure centers and trigger dopamine release — the same chemical involved in reward and addiction. Its creamy texture, sweetness, and fat content make it a sensory powerhouse that keeps the brain coming back for more.
5. Ice Cream: The Dopamine Double-Whammy
Ice cream combines sugar and fat in perfect harmony to light up the brain’s reward system. A 2012 study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that frequent consumption can dull the brain’s pleasure response, leading people to eat more to feel satisfied — just like tolerance seen in drug use.
4. Donuts: Sugar-Coated Addictive Bombs
A donut’s mix of refined flour, sugar, and fats spikes blood sugar and floods the brain with dopamine. When the inevitable crash follows, cravings intensify. This “reward-crash” cycle mirrors the short-lived highs of drug addiction.
3. Cheesy Foods: The Casein Connection
Cheese and cheese-based favorites — pizza, snacks, mac & cheese — contain casein, a milk protein that releases casomorphins during digestion. These compounds bind to the brain’s opioid receptors, releasing dopamine and creating pleasure. Combined with high fat and salt, cheese keeps taste buds hooked.
2. Candy and Sugary Drinks: The Hidden Addictions
Pure sugar floods the bloodstream quickly, producing an instant dopamine rush. Over time, this rewires the brain’s addiction pathways, increasing cravings similar to those triggered by alcohol or opioids.
1. Oreo Cookies: The Ultimate Craving
A 2013 Connecticut College study found that rats reacted to Oreos the same way they did to cocaine or morphine. The cookies activated more neurons in the brain’s pleasure center than the drugs themselves — proof that ultra-processed foods can be powerfully addictive.